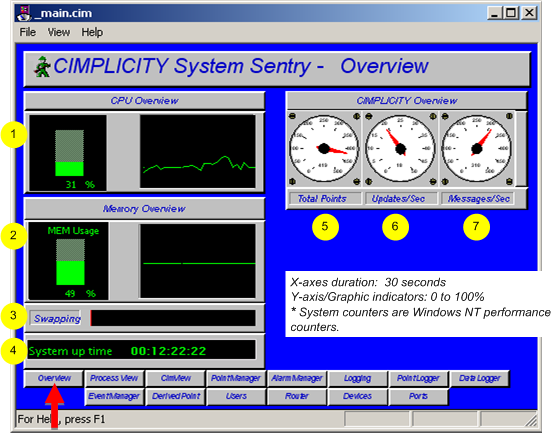
The Overview screen provides a general view of the computer and CIMPLICITY's performance.
|
1 |
System's current % CPU use. |
|
2 |
System's current memory usage. |
|
3 |
System memory swapping*. |
|
4 |
Time is days:hours:minutes:seconds since the system booted up. |
|
5 |
Total points in the current CIMPLICITY project. |
|
6 |
Total point updates/sec. |
|
7 |
Messages in and out of CIMPLICITY. |
![]() Guidelines for reading the Overview screen
include:
Guidelines for reading the Overview screen
include:
![]() Review the CPU Overview for:
Review the CPU Overview for:
![]() Current CPU Utilization
Current CPU Utilization
![]() Trend of CPU usage.
Trend of CPU usage.
The steady state CPU Usage should be below 60% for a non-redundant project and below 45% for a redundant project.
Do not let your system become fully utilized. A lower utilization enables CIMPLICITY to respond in a timely manner to events in your process. This is particularly critical when using redundancy.
When your computer is over-utilized, you have two choices:
Replace it with faster hardware.
Reduce the software load on the system. To do this you need to identify what Process is using the majority of the CPU time. The System Sentry Process Screen can provide you with this information. Some typical ways to reduce CPU utilization are:
Reduce Device Communications Scan Rate (Port Configuration).
Reduce Database Logging frequency.
Reduce the number of points.
![]() Review the Memory Overview for:
Review the Memory Overview for:
![]() Current memory utilization
Current memory utilization
![]() Trend of memory utilization
Trend of memory utilization
As with excessive CPU utilization, excessive memory utilization will degrade system performance.
As a rule-of-thumb, the
Steady-state memory utilization should not exceed 75%.
To increase virtual memory
Open the Microsoft Windows Control Panel
Select System.
Select the Performance tab.
Use Microsoft Help for details on how to adjust the virtual memory size, which should be twice as high as physical memory.
Note: increasing virtual memory size will not reduce swapping if it is occurring. It simply gives the computer more memory "headroom."
![]() Swapping indicator should
indicate no swapping while running in a steady state (EX. not
opening new applications).
Swapping indicator should
indicate no swapping while running in a steady state (EX. not
opening new applications).
Swapping occurs because there is not enough physical memory in the computer and memory is swapped to disk. This rule-of-thumb is most important because a system that is constantly swapping will exhibit poor performance.
Two ways to reduce swapping are:
Add more physical memory to the computer.
Decrease the memory being used by applications on computer.
![]() Check System Disk Usage for the amount disk
space being used. Running out of disk space will cause application
problems. Therefore, you must maintain free disk space on the
computer.
Check System Disk Usage for the amount disk
space being used. Running out of disk space will cause application
problems. Therefore, you must maintain free disk space on the
computer.
|
System Sentry screens list. |