Data tokens are dynamic tokens that are replaced by production data during runtime.
The 3 types of data tokens that are available for use in ASCII forms are:
Tracker attributes.
Tracker extended attributes.
Solve results.
|
Data token types. |
|
|
Sub-string description. |
|
|
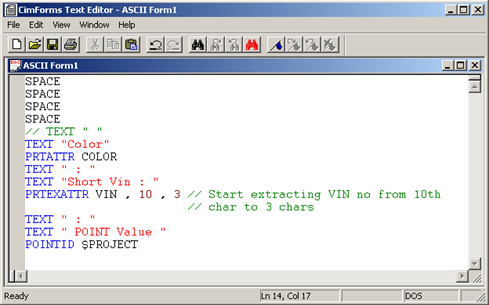
Data token example |
Data token types are:
|
Token Type |
Description |
|
PRTATTR |
Tracker attribute data token. We were looking at two different token names, but in the product the user will have only one token name. Example PRTATTR <VINNO> Where <VINNO> is the name of a Tracker attribute defined in the Tracker model. |
|
PRTEXATTR |
Tracker Extended attribute data token. Example PRTEXATTR <SHORTVIN> Where <SHORTVIN> is the name of a Tracker extended attribute, which is defined in the Tracker model. |
|
SOLVE |
Solve data token representing the result of a value solve. Example SOLVE <Solvename:Solvemethod> Example SOLVE <$GETVALA$;getvalues> Where $GETVALA$ is solve name and getvalues is a solve method. |
|
POINTID |
Point ID data token. Example POINTID <$PROJECT> Where $PROJECT is the Point Id , which is a defined Point in the Workbench. |
Sub-string description
The data tokens types can also be used as follows:
XXXX yyy , a, b
Where
|
Code |
Description |
|
XXXX |
Any of the four data tokens
|
|
yyy |
Any of the following.
|
|
a |
(Optional) starting character If a is not given, the whole string is returned. |
|
b |
(Optional) count of characters to extract starting from a. If b is not given, then starting from a a While string is returned. |
![]() Note: The user cannot
add a List Solve to the ASCII forms. A Boolean solve can be used
with conditional tokens.
Note: The user cannot
add a List Solve to the ASCII forms. A Boolean solve can be used
with conditional tokens.
Data token example
|
Step 3.2.1. Use pre-defined tokens. |