| Applies To: |
|
| Summary: |
| What is the difference between Basic
Authentication and Windows Integrated Authentication? How do I
enable Windows Integrated Authentication with Citect Web
Client? |
| Solution: |
| Authentication is required to access a web
server over Intranet or Internet when the resources on the system
are not made available on the public domain but rather only to
approved users. Of the four different types of authentication, this
document only compares two major types, Basic Authentication and
Windows Integrated Authentication, and their use with the
CitectSCADA Web Client. These two types of Authentication are
outlined below as per Microsoft Knowledge Base Article 324276, at
the URL http://support.microsoft.com/kb/324276/en-us at the time of
writing. Basic Authentication This type of authentication requires the user to enter a user ID and a password. This provides a low level of security. User credentials are sent in clear text across the network. This format provides a low level of security because the password can be read by almost all protocol analysers. However, it is compatible with the widest number of Web clients. This option is best used when you want to grant access to information with little or no need for privacy. Because user credentials are encoded with Base64 encoding but they are not encrypted when they are transmitted over the network, basic authentication is not considered a secure form of authentication. Windows Integrated Authentication This type of authentication is more secure than basic authentication, and it functions well in an intranet environment where users have Windows domain accounts. In integrated Windows authentication, the browser tries to use the current user's credentials from a domain logon, and if this attempt is unsuccessful, the user is prompted to enter a user name and password. If you use integrated Windows authentication, the user's password is not transmitted to the server. If the user has logged on to the local computer as a domain user, the user does not have to authenticate again when the user accesses a network computer in that domain. Note that you must use Microsoft Internet Explorer 2.0 or later as your Web browser if you are using Windows Integrated authentication (Please note that you will need a minimum of Windows IE 6 to use Citect Web Client). Enabling Windows Integrated Security on the CitectSCADA Web Server Enabling Windows Integrated Security would first of all require the user to log on as an Administrator or as a user with Administrative privileges on the computer acting as the web server. Go through the Web Client- Quick Start v1.doc and create 'testdisplay', 'testmanager' and 'webclientadmin' users and add them to their respective groups. Also add a user who has access to the domain via a user ID and Password. 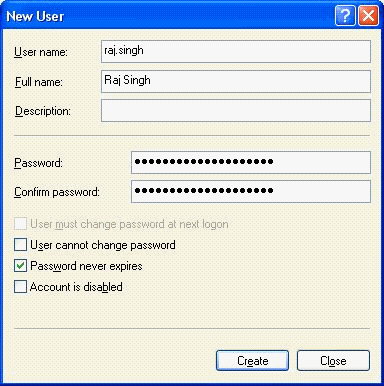
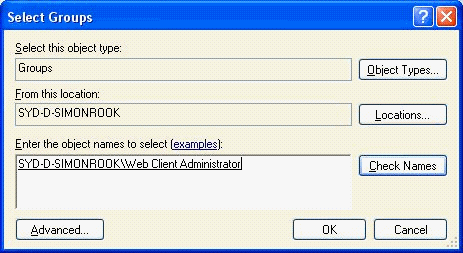
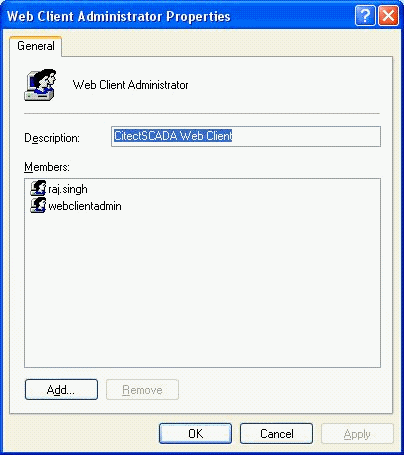
Add the user (in this instance “Raj.Singh) to the group 'Web
Client Administrator' on the Web Server (in this instance
SYD-D-SIMONROOK).
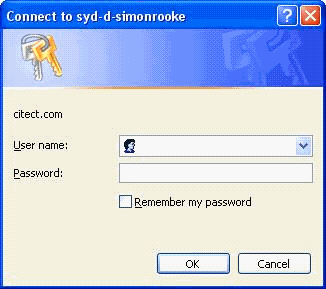
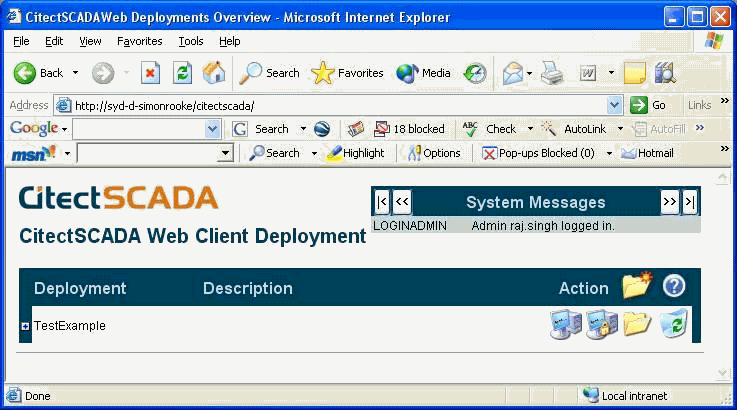
Enter the login details for the user. Once the user credentials
are verified the screen that is supposed to appear is shown
below.
Expand Server_name (which in this case is SYD-D-SIMONROOK) and
then expand Web Sites. Right select the CitectSCADA virtual
directory and select Properties.
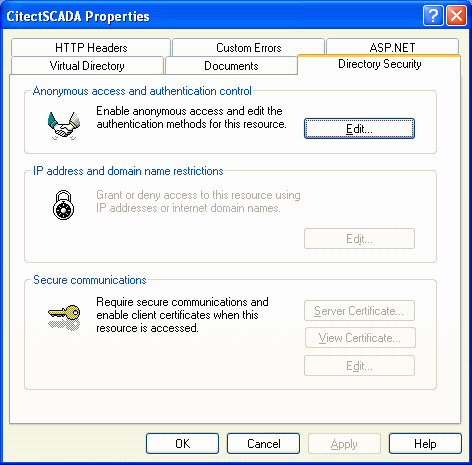
Select the Directory Security tab and click on Edit to edit the
Authentication control.
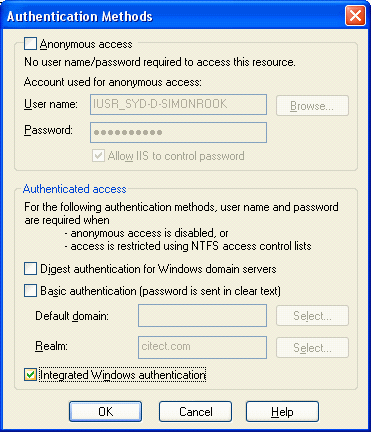
On Authentication Methods window, uncheck Basic Authentication
and check Integrated Windows Authentication.
Reboot both PCs (server and client). On restart, the user (in this case Raj.Singh) will be able to view the Web Client admin page from his client PC without having to enter his username and password. That is, he could access the page via Integrated Windows Authentication. |
| Keywords: |
| Windows Authentication, web client, security |
Related Links
Attachments