Deviation alarming is used to detect when the value of a point deviates too far from that of a second point.
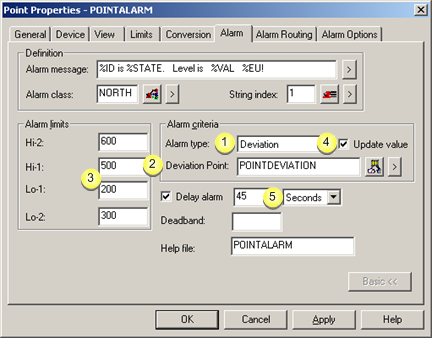
|
Alarm type |
|
|
Deviation Point |
|
|
Alarm limits |
|
|
Update value |
|
|
Delay alarm |
|
Alarm type |
Select Deviation for deviation alarming.
|
Deviation Point |
Deviation point values are used to calculate a deviation from the norm.
An alarm is generated when the difference between the current value of the point and the current value of the Deviation point exceeds an alarm limit.
This difference is calculated whenever the value of the point or the Deviation Point changes.
|
|
Opens the Select a Point browser to select an available point. |
|
|
Displays a Popup menu to: |
||
|
|
|
|
|
Alarm limits |
Alarm limit values are based on the deviation from the norm, where the:
![]() High limit is larger than the
Warning High limit.
High limit is larger than the
Warning High limit.
![]() Low limit is larger than the
Warning Low limit.
Low limit is larger than the
Warning Low limit.
|
An alarm is generated when the: |
Difference between the current value of the point and the current value of the Deviation Point exceeds an alarm limit. |
This difference is calculated whenever the value of the point or the Deviation Point changes.
Note: Alarm limits field names are determined by the selected string index.
|
Limit |
Value |
Description |
|
Hi-2 |
600 |
Furthest from the norm. |
|
Hi-1 |
500 |
Lower than Hi-2. |
|
Normal |
Limits are based on the deviation from the norm. |
|
|
Lo-1 |
200 |
Lower than Lo-2. |
|
Lo-2 |
300 |
Furthest from the norm |
|
Update Value |
(Optional) If %VAL is in the Alarm message:
|
Check |
Updates the value in the alarm message during runtime, when the value changes. |
|
Clear |
Does not update the value in the alarm message during runtime, when the value changes. |
|
Delay alarm |
(Optional) Delays the display of the alarm on Alarm Viewers and other Alarm Management Interested Processes unless the point remains in an alarm state for the configured interval.
The point is scanned at its normal Scan Rate , but is evaluated for alarming at the Alarm Delay rate (also known as the sample interval).
|
When an alarm condition is |
The Point Manager sends the information: |
|
|
No Alarm delay is configured |
Immediately to the Alarm Manager and all other Point Management Interested Processes such as CimView and the Event Manager. |
|
|
An Alarm delay is configured |
After the delay time generates the Alarm Delay. This means that Alarm Delay applies to all the Point Management Interested Processes such as CimView, Point Control Panel and the Event Manager, the Alarm Viewer and other Alarm Management Interested Processes, such as the Alarm Printer, that are serviced by the Alarm Manager. |
|
|
Check box |
Check to display the length and interval fields. |
|
|
Length |
Length of selected interval time to delay the display. |
|
|
Interval |
Options are:
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
![]() Note: If the point has:
Note: If the point has:
![]() Engineering units (EU)
and
Engineering units (EU)
and
![]() Deviation alarming,
Deviation alarming,
an alarm is generated when the difference between the:
![]() Current converted value of
the point and
Current converted value of
the point and
![]() Converted value of the
deviation point (if the deviation point also has EU)
Converted value of the
deviation point (if the deviation point also has EU)
exceeds an alarm limit.
|
Step 3.2.2. Select alarm criteria. |