Circular Redundancy |
|
zenon network -> The multi-server network -> Special requirements for the integration project -> Circular Redundancy |
  |
Circular Redundancy |
|
zenon network -> The multi-server network -> Special requirements for the integration project -> Circular Redundancy |
  |
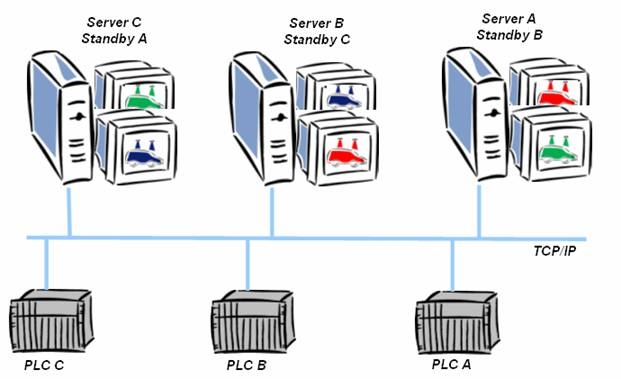
Circular Redundancy is a unique technology to efficiently combine several redundant projects. The Circular Redundancy combines the functionalities multi-project administration and redundancy to a cost effective possibility to increase equipment availability.
For redundant projects, you usually need two PCs. One PC is the server, the other one is the standby. For two projects you need four PCs, and so on.
Circular Redundancy, however, uses the possibilities offered by the multi-project administration: Several projects can run simultaneously on one PC. Each PC is the server for one project and at the same time the standby server for the neighboring project; and additionally, it can be the client for other projects. This forms a circle.
This offers an enormouse potential for cost reduction for both hardware and software. Instead of 4, 6, or 8 PCs and licences you now only need half.
|
|
|
In your production hall for car care products, there are three machines. The first produces the care product, the second bottles it and the third packages the bottles for the transport. On each machine, a visualization program runs as a server project. For a redundant system, you would need six PCs. But not with Circular Redundancy: On each PC, a second project runs as standby: On the production machine for the bottling project, on the bottling machine for the packaging project and on the packaging machine for the production project. So each project is redundant. If one PC fails, the other two offer the full functionality. You have increased the availability, no data are lost in case of server failure or maintenance work, and you additionally saved money. |